Tropical Forest Canopy Height: Impacts of Climate Change
Tropical forest canopy height plays a crucial role in understanding the health and dynamics of these vital ecosystems. As towering trees form the upper layer of these lush environments, they significantly contribute to carbon storage, thus serving as essential buffers against climate change. NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) leverages advanced laser technology to provide unprecedented insights into how variations in canopy height reflect environmental shifts. This groundbreaking study not only highlights the impacts of dryness and temperature on canopy structure but also emphasizes the interconnectedness of forest health with climate resilience. Understanding these dynamics is vital as we navigate the future of our planet’s climate and work towards effective conservation strategies.
The height of the canopy in tropical woodlands is an indication of the ecological balance within these verdant habitats. These forests, often regarded as the lungs of the Earth, are vital for capturing carbon dioxide and supporting biodiversity. Recent advancements in technology, particularly through initiatives like NASA’s GEDI, have allowed researchers to delve deeper into the environmental factors influencing tree height and forest stability. By exploring the intricate relationships between canopy elevation and climate variations, scientists can better assess the resilience of these ecosystems in the face of ongoing climate adversities. The health of tropical ecosystems is not just a local concern; their integrity affects global environmental conditions and climate policies.
Understanding the Significance of Tropical Forest Canopy Height
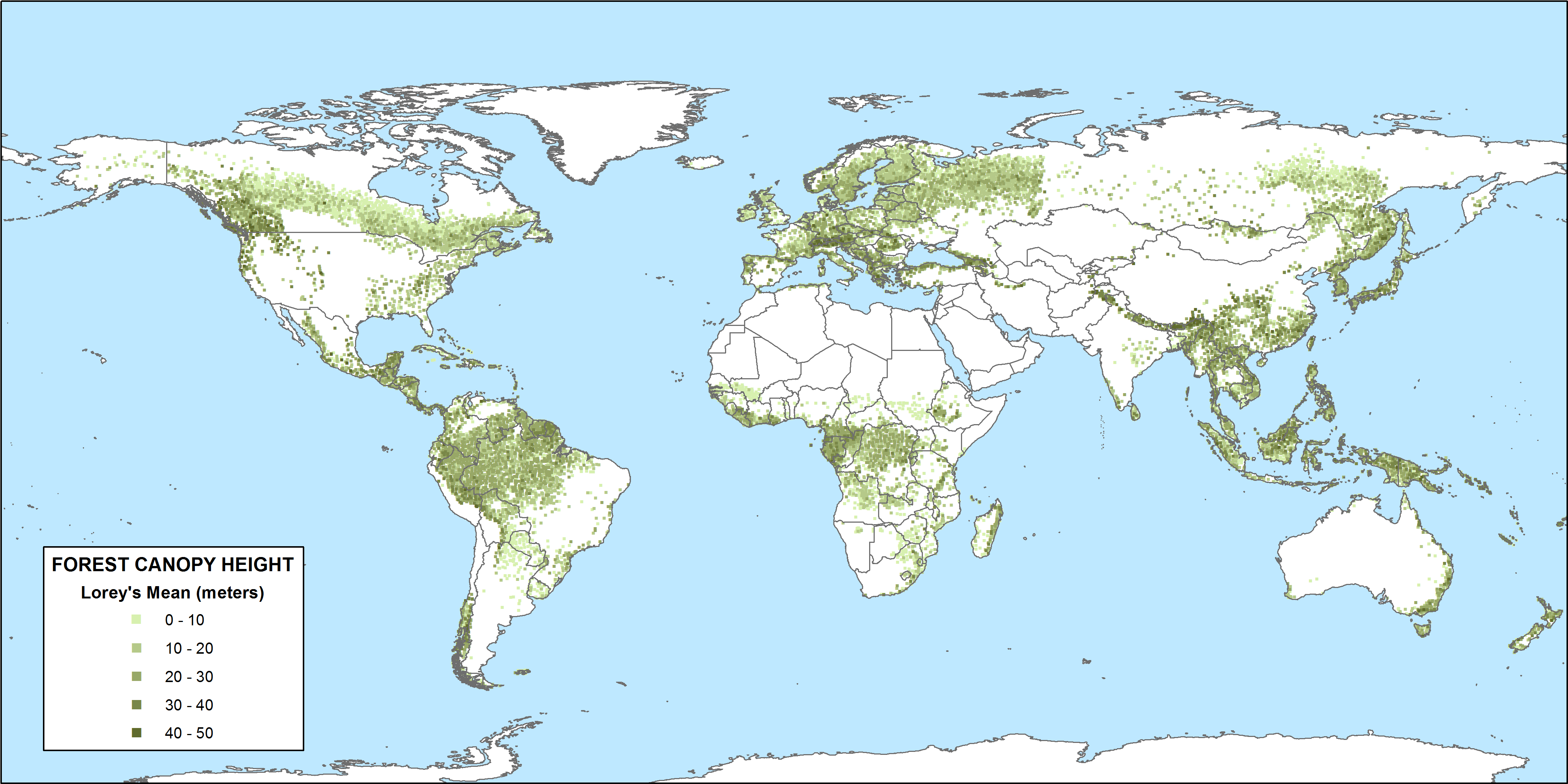
The tropical forest canopy height serves as a vital indicator of ecosystem health and productivity. Scientists have long recognized that the structure of the canopy is intricately linked to key ecological processes, including carbon storage. Taller canopies often correlate with a higher concentration of biomass, which is essential for mitigating climate change through increased carbon sequestration. By utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology, researchers have been able to collect data on canopy height variations across different regions, providing crucial insights into how tropical forests respond to environmental drivers such as temperature and moisture.
Moreover, the implications of canopy height extend beyond mere measurements; they provide an understanding of how forests interact with their surroundings. Tall canopies play a critical role in buffering microclimates, which can help reduce extreme temperatures during heat events. As climate change threatens to alter these dynamics, it becomes imperative to monitor the health of the forests to ensure their continued ability to function as carbon sinks. This data not only aids in forecasting future changes but also highlights areas in need of conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of tropical forest canopy height in assessing forest health?
Tropical forest canopy height is a critical indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity. Taller canopies are generally associated with higher carbon storage and greater above-ground biomass, which enhances forest resilience to climate change impacts.
How does climate change affect tropical forest canopy height?
Climate change significantly impacts tropical forest canopy height through variables like prolonged dry seasons and increasing temperatures. Research utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology has shown that these environmental changes can lead to significant reductions in canopy height, particularly in vulnerable areas such as the southern Amazon.
What technology does NASA use to measure tropical forest canopy height?
NASA uses the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI), a LiDAR laser instrument aboard the International Space Station, to measure and monitor tropical forest canopy height. This technology allows for detailed analysis of forest structure and health globally.
Why is monitoring tropical forest canopy height important for carbon storage assessments?
Monitoring tropical forest canopy height is essential for carbon storage assessments as taller canopies typically correlate with higher levels of carbon sequestration. Understanding canopy dynamics helps in estimating the carbon storage capacity of different tropical forest regions.
How do variations in topography affect tropical forest canopy height?
Topography plays a significant role in determining tropical forest canopy height. Factors such as elevation, dry season length, and solar radiation contribute to nearly three-quarters of the variation in canopy height across differing regions, as shown in studies using NASA GEDI data.
What have recent studies revealed about the factors influencing tropical forest canopy height?
Recent studies, including those using NASA’s GEDI, have revealed that climate variables, topography, and soil properties are key factors influencing tropical forest canopy height. Understanding these drivers aids in assessing forest health and potential responses to climate change.
What role do tropical forests play in mitigating climate change?
Tropical forests are crucial for mitigating climate change as they not only serve as biodiversity hotspots but also play a vital role in carbon storage. Protecting and understanding these forests is essential for effective climate change policies and strategies.
How can policymakers benefit from understanding tropical forest canopy height?
Policymakers can benefit from understanding tropical forest canopy height by identifying vulnerable areas that require protection. This knowledge is critical in developing effective conservation strategies and policies aimed at enhancing carbon storage and forest resilience against climate change.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Tropical Forest Canopy Height | An important measure of forest health and ecosystem productivity, affected by climate change. |
| Use of NASA Technology | NASA GEDI (Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation) LiDAR technology assesses canopy height changes globally. |
| Impact of Climate Change | Climate, topography, and soil properties account for up to 75% of canopy height variation. |
| Vulnerability | Tropical forests in southern Amazon are particularly vulnerable due to prolonged dry seasons. |
| Policy Implications | Understanding canopy height changes aids in carbon sequestration strategies and conservation policies. |
| Future Research | Expansion of study beyond primary forests to include more woodlands to inform climate policy. |
Summary
Tropical forest canopy height is a critical indicator of the health of these ecosystems. The study highlighted the vulnerability of tropical forests, especially in regions like the southern Amazon, to the adverse effects of climate change. By utilizing advanced NASA technology, researchers have gained an unprecedented understanding of how factors like climate, topography, and human activity impact canopy height. This knowledge is crucial not only for conserving biodiversity but also for enhancing global carbon storage efforts. Protecting tropical forests emerges as an essential strategy in mitigating climate change effects.